Depression is one of the most common psychiatric disorders, yet it can be challenging to diagnose. There are no blood tests or brain scans that confirm it. Instead, diagnosis is based on clinical evaluation.
Typically, at least two primary and two secondary symptoms must be present for a minimum of two weeks. Psychiatrists also consider the patient’s recent emotional history and the impact of symptoms on daily functioning. Physical complaints—such as heart palpitations or breathing difficulties—are also evaluated, as they can be linked to depression.
XXX
With a lifetime prevalence of 10 to 18 percent and a point prevalence of up to seven percent, depressive disorders are among the most common illnesses. Women are affected about twice as often as men. In 50 percent of patients, the first episode occurs before the age of 32. First manifestations in childhood and adolescence are also common. By contrast, first onset after the age of 56 is relatively rare, accounting for about ten percent of cases. However, in older patients these disorders present particular challenges because of the frequent presence of somatic comorbidities.
In approximately 50 to 60 percent of affected individuals, depression is the only psychiatric disorder. In the remaining patients, complex patterns of comorbidity with other mental disorders are common. Such comorbid conditions are associated with greater illness severity, reduced psychosocial functioning, and a less favorable prognosis.
Because of their frequency and severity, depressive disorders are listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) among the leading causes of disability worldwide.
The following review article focuses on the diagnosis of depression.
Diagnosing Depression at CHMC in Dubai
At CHMC Dubai, we take a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and treating depression. Because many depressive symptoms overlap with other mental and physical conditions, a careful assessment is essential before confirming the diagnosis.
We base our evaluations on internationally recognized criteria, including the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). This ensures accuracy and allows us to design a personalized treatment for depression that addresses both emotional and physical symptoms.
Our goal is not only to help patients recover from current symptoms but also to equip them with tools and strategies to maintain long-term mental health.
Steps in Diagnosing Depression at CHMC
Recognizing depression isn’t always straightforward. Many people experience emotional numbness or struggle to describe their feelings. Others present with vague physical complaints—such as headaches, fatigue, or digestive discomfort—without realizing these could be symptoms of depression. Therefore, accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective treatment for depression.
At CHMC Dubai, our process begins with a thorough psychiatric evaluation carried out by an experienced psychiatrist or psychologist. In some cases, the first step may be the simple but effective Two-Question Test, which can quickly indicate whether further assessment is needed.
The Two-Question Test
A quick screening tool often used in the early stages of assessment is the Two-Question Test:
- Have you frequently felt down, sad, or hopeless in the past month?
- Have you noticed a loss of interest or pleasure in activities you usually enjoy over the past month?
A “yes” to both questions suggests possible depression, prompting a more detailed evaluation of symptoms and their impact on daily life.
Initial Patient Conversation (Anamnesis)
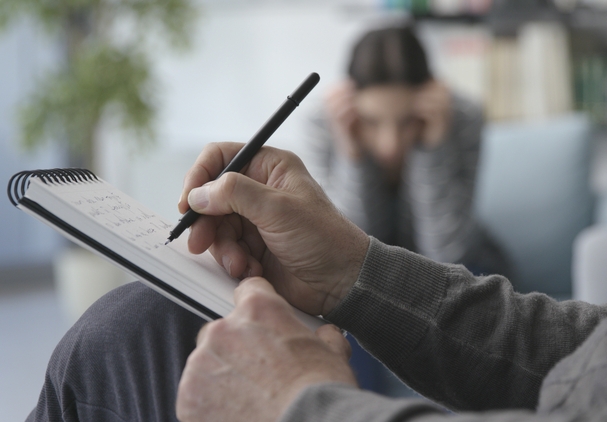

The core of diagnosing depression lies in the conversation between the patient and the clinician. An open, honest discussion enables the psychiatrist or psychologist to assess the severity of symptoms and gain a clear understanding of the patient’s overall emotional state.
The conversation may follow a structured format with specific questions, or it may take a more open-ended approach—inviting the patient to share why they sought help, how they’ve been feeling, and what challenges they’re facing. Flexibility is important, as patients sometimes begin by discussing unrelated but significant life events or personal struggles.
During this exchange, clinicians also note subtle indicators: tone of voice, facial expressions, posture, and even clothing choices. A quiet voice, lack of emotional expression, or slouched posture can all signal depressive symptoms.
In complex cases—such as patients with severe medical conditions, coexisting mental disorders, or elderly individuals—speaking with family members or caregivers can provide valuable additional insights.
Physical Examinations and Routine Diagnostics at CHMC Dubai
A physical exam is an important step in ruling out medical conditions that can mimic depression. This may include:
General Physical Exam
assessing overall health to identify possible contributing factors.
Neurological Exam
checking for central nervous system disorders that could cause similar symptoms.
Laboratory Tests
Lab tests help evaluate the patient’s physical health before starting any medication as part of their treatment for depression. These results also serve as a baseline for monitoring progress and possible side effects.
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
An ECG is performed to detect any underlying heart conditions before beginning certain antidepressant medications. The initial ECG provides a reference point for future check-ups during treatment.
Additional Diagnostics in Treatment of Depression
In cases involving severe mental health disorders—such as psychosis or bipolar disorder—further neurological investigations may be needed. These can include:
CT or MRI Brain Scans
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are special types of examinations that allow detailed images of organs and body tissues, such as the brain. CT uses X-rays, while MRI works with the help of a strong magnetic field.
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
Electroencephalography, or EEG for short, is a diagnostic procedure used to record the brain’s electrical currents (changes in potential). These are displayed as brain waves on a graph, representing the combined electrical activity of the nerve cells. The actual result is called an electroencephalogram. The recording is made using electrodes placed on the scalp, which continuously detect, amplify, and record the brain’s potential fluctuations, known as brain waves.
By following these steps, CHMC Dubai ensures each patient receives a precise diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan for depression that addresses both the psychological and physical aspects of the condition.


